Polymer adhesion was caught in time to prevent valve malfunction
By tracking parameters that indicated valve sticking, the buildup of polymer inside the control valve was detected, preventing the malfunctions and sticking that could otherwise have occurred.
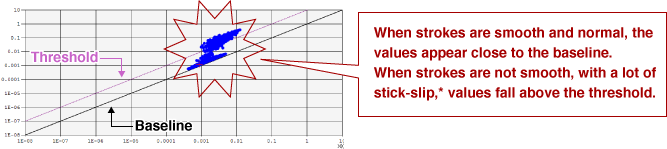
Checking of the stick-slip monitoring screen
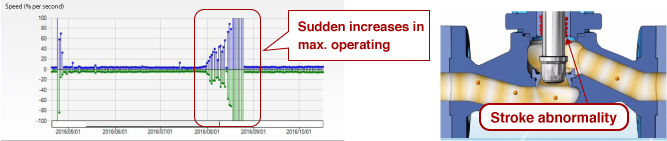
Checking the maximum operating speed monitoring screen
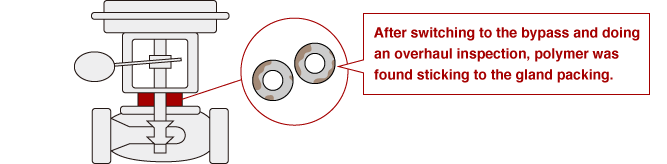
Switch to the bypass and do an overhaul inspection
* Stick-slip is when the valve shaft repeatedly sticks and then slips during a stroke.
This causes increases in the shaft’s operating speed.
At this chemical plant, stick-slip occurs when polymerization progresses inside control valves.
Abnormalities in the instrument were detected before the process was affected
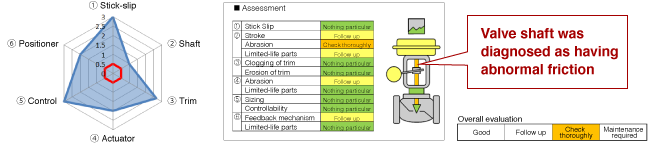
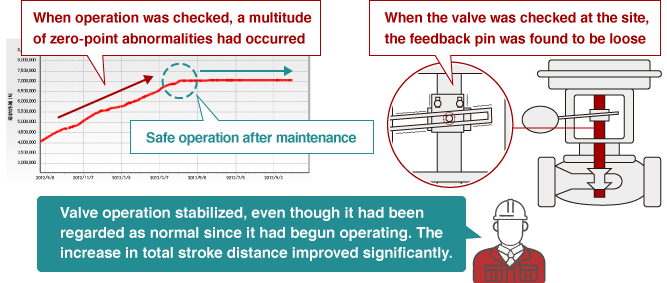
A valve shaft was diagnosed as behaving abnormally, leading to an inspection where the feedback pin was found to be loose. Since there were no problems with controllability and no process alarms were generated, the loose feedback pin could have been overlooked.
Checking the assessment results in the valve diagnosis report
On-site check
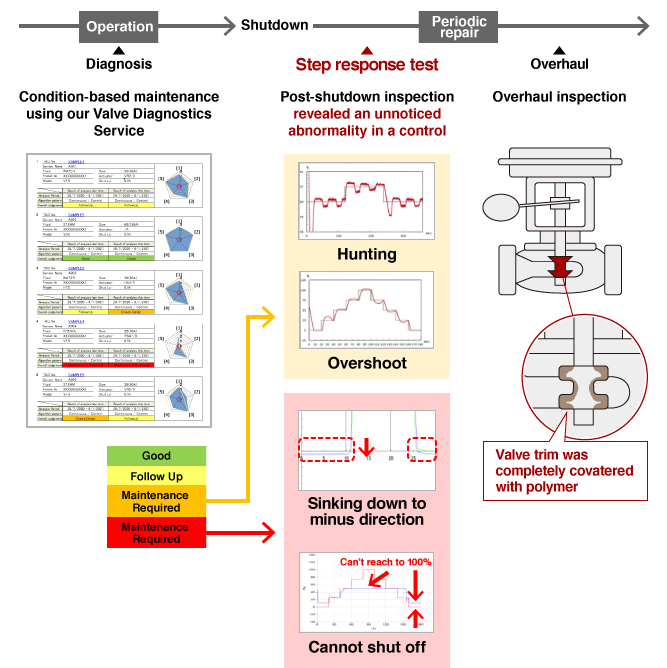
Optimizing the selection of valves for maintenance
During advance diagnosis, a valve that was not scheduled for repair under the regular time-based maintenance plan was diagnosed as “Maintenance required” and “Check thoroughly.” A step response test revealed something abnormal, and the diagnosis was verified in an overhaul inspection. Were it not for the diagnosis, a “sudden” problem would have occurred later at startup or during operation.
Inquiries